Have you ever wondered what makes the raw material for your 3D printer tick? Understanding the different types of FDM 3D printing filament is critical to achieving optimal results in your 3D printing projects. This comprehensive guide breaks down various filament types, their key features, and considerations you need to bear in mind to select the ideal material for your needs.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
What is 3D Printing Filament?
3D printing filament is the thermoplastic feedstock used in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers. These thermoplastics are heated to a semi-liquid state and extruded layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. The choice of filament impacts the print quality, durability, flexibility, and application of the final product. Let’s explore the types of 3D printer filaments to help you make informed decisions for your printing projects.

This image is property of coprint3d.com.
Types of 3D Printer Filaments
ABS Filament (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Key Features of ABS Filament
Durability: ABS filament is known for its high durability and impact resistance. This makes it suitable for producing robust and long-lasting parts.
Applications: Common applications include automotive parts, household appliances, and LEGO bricks.
Printing with ABS: ABS requires a heated bed to prevent warping and benefits from an enclosed printing environment to manage temperature fluctuations.
ASA Filament (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
Key Features of ASA Filament
Durability: ASA is similar to ABS but offers better UV resistance, making it more suitable for outdoor applications.
Applications: It’s used in automotive parts, outdoor furniture, and sports equipment.
Printing with ASA Filament: ASA also requires a heated bed and performs best in an enclosed chamber to reduce warping.
PLA Filament (Polylactic Acid)
Key Features of PLA Filament
Durability: PLA is less durable than ABS but more user-friendly due to its ease of printing. It’s biodegradable, making it environmentally friendly.
Applications: Used in prototypes, educational projects, and low-stress applications.
Printing with PLA Filament: PLA does not necessarily require a heated bed, making it easier for beginners to use.
PET Filament (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
Key Features of PET Filament
Durability: PET is a durable, clear filament with excellent chemical resistance.
Applications: Ideal for food containers, automotive parts, and mechanical components.
Printing with PET Filament: A heated bed is recommended, and PET prints well with minimal warping.
PETG Filament (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Key Features of PETG Filament
Durability: Combines the best properties of PLA and ABS, offering durability and ease of printing without brittleness.
Applications: Used in water bottles, mechanical parts, and medical devices.
Printing with PETG Filament: A heated bed is necessary, and PETG offers great layer adhesion and minimal warping.
PC Filament (Polycarbonate)
Key Features of PC Filament
Durability: Exceptionally strong, highly resistant to impact, and maintained across a wide range of temperatures.
Applications: Used in automotive parts, electronic housings, and bulletproof glass.
Printing with PC Filament: Requires high printing temperatures and a heated bed, often needing an enclosed build chamber for best results.
PP Filament (Polypropylene)
Key Features of PP Filament
Durability: Offers high chemical resistance and is flexible, making it suitable for living hinges and similar features.
Applications: Used in automotive parts, packaging materials, and medical products.
Printing with PP Filament: Requires careful bed preparation to ensure adequate adhesion.
Nylon Filament (PA)
Key Features of Nylon Filament
Durability: Nylon is known for its high impact resistance, flexibility, and abrasion resistance.
Applications: Ideal for gears, mechanical parts, and bearings.
Printing with Nylon Filament: A heated bed is necessary, and it often requires control of humidity levels due to its tendency to absorb moisture.
Carbon Fiber Filament
Key Features of Carbon Fiber Filament
Durability: Combines the strength of carbon fiber with the flexibility of base thermoplastics, resulting in lightweight yet strong parts.
Applications: Used in aerospace, automotive, and high-stress mechanical applications.
Printing with Carbon Fiber Filament: Requires hardened nozzles due to abrasive nature, with a heated bed recommended.
CPE (Polyvinyl Alcohol) Filament
Key Features of CPE Filament
Durability: Offers excellent chemical resistance and strong layer adhesion.
Applications: Used in chemical containers, mechanical parts, and aesthetic models.
Printing with CPE Filament: Often requires a heated bed and benefits from minimal moisture exposure.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) Filament
Key Features of PEEK Filament
Durability: PEEK offers superior mechanical properties and excellent chemical resistance, even at high temperatures.
Applications: Used in aerospace, medical implants, and automotive components.
Printing with PEEK Filament: Demands extremely high printing temperatures and a heated bed, often requiring advanced 3D printers.
POM (Polyoxymethylene) Filament
Key Features of POM Filament
Durability: POM is known for its excellent stiffness, low friction, and high dimensional stability.
Applications: Common in gears, automotive components, and industrial applications.
Printing with POM Filament: Requires a heated bed and good ventilation due to potentially harmful off-gassing during printing.
PMMA (Acrylic) Filament
Key Features of PMMA Filament
Durability: Offers high transparency and impact resistance, making it a good alternative to glass.
Applications: Used in lighting fixtures, display windows, and optical devices.
Printing with PMMA Filament: Requires a heated bed, and best results are achieved with careful control of printing temperatures.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Filament
Key Features of PVC Filament
Durability: PVC is known for its toughness, chemical resistance, and flame retardance.
Applications: Common in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, and protective housings.
Printing with PVC Filament: Requires precise temperature control and good ventilation due to potentially harmful fumes.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) Filament
Key Features of TPU Filament
Durability: Offers excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and shore hardness customization.
Applications: Ideal for flexible hoses, gaskets, and wearable parts.
Printing with TPU Filament: Requires a slow print speed and good bed adhesion, often with a heated bed.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) Filament
Key Features of TPE Filament
Durability: Extremely flexible and resilient, making it suitable for applications requiring rubber-like elasticity.
Applications: Used in phone cases, medical devices, and flexible seals.
Printing with TPE Filament: Slower print speeds and a heated bed help ensure successful prints.
HIPS (High-impact Polystyrene) Filament
Key Features of HIPS Filament
Durability: Similar to ABS in strength but with the added benefit of being dissolvable in Limonene.
Applications: Used for support material when printing complex geometries and non-technical prototypes.
Printing with HIPS Filament: Prints well with similar settings as ABS, making it suitable for dual-extrusion printers.
Metal Filament
Key Features of Metal Filament
Durability: Combines the properties of metals like copper, steel, or bronze with the ease of 3D printing thermoplastics.
Applications: Used in jewelry, decorative items, and functional prototypes that require metal properties.
Printing with Metal Filament: Requires hardened nozzles due to the abrasive nature and may necessitate post-processing to achieve desired finishes.
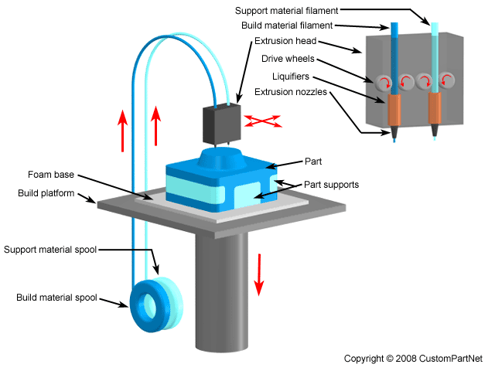
This image is property of www.3devo.com.
Choosing the Right Filament for the Job
Selecting the appropriate filament depends on the specific requirements of your project. Understanding the characteristics of each type of filament helps you make an informed decision. Factors such as required mechanical properties, intended application, environmental conditions, and printer compatibility should guide your choice. For instance, if you need a durable outdoor component, ASA would be suitable due to its UV resistance. Conversely, for simple prototyping, PLA might be the best option due to its ease of use.

This image is property of i.all3dp.com.
Key Considerations for 3D Printer Filament Choice
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility are crucial. For load-bearing parts, materials like ABS or Nylon may be appropriate. For flexible components, TPU or TPE would be more suitable.
Thermal Properties
The filament’s ability to withstand high or low temperatures without deformation is essential in applications like automotive or aerospace. Filaments like PC and PEEK have excellent thermal stability.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance is vital for parts that will be exposed to harsh environments. Materials like PETG and PP offer good chemical resistance and are suitable for such situations.
Electrical Properties
Electrical applications may require filaments with specific insulating or conductive properties. Consider materials like Nylon for its good electrical insulation properties.
Biocompatibility
For medical and pharmaceutical applications, biocompatible materials are necessary. PLA and some grades of PETG are known for their biocompatibility.
Aesthetic Requirements
The appearance of the final product may dictate the choice of filament. PMMA offers high transparency for optical applications, while PLA comes in a wide range of colors.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to UV light, moisture, and other environmental conditions can degrade certain filaments. ASA is UV resistant, making it ideal for outdoor use.
Regulatory Compliance
For parts that must adhere to specific regulatory standards, ensure the filament used complies with relevant certifications. PEEK, for example, is often FDA-approved for medical use.
Post-Processing
Some filaments offer better post-processing capabilities, such as sanding and painting. ABS can be easily post-processed but emits fumes requiring proper ventilation.
Printer Compatibility
Compatibility with your 3D printer is crucial. Some advanced filaments require specialized printers, extruders, or build chambers.
Cost and Availability
The cost and availability of the filament may also impact your choice. Basic filaments like PLA are widely available and affordable, while high-performance materials like PEEK are more expensive and harder to source.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the most suitable material that will ensure the success of your 3D printing project. This guide aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of FDM 3D printing filaments, helping you make informed decisions for your projects.

This image is property of racheldebarros.com.
3D Printing FDM Filament Guide
Understanding and choosing the right filament is essential for optimizing your 3D printing experience. This guide has covered a wide range of materials, their key features, and considerations to take into account when selecting filament. With this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the world of FDM 3D printing and achieve the best possible results in your projects.
