Have you ever wondered what makes a 3D printer tick? If you’re considering diving into the world of hobby 3D printing, understanding the parts of a 3D printer will give you a solid foundation for your adventures in creating three-dimensional objects. Let’s go on a journey to explore the various components that come together to make 3D printing possible.
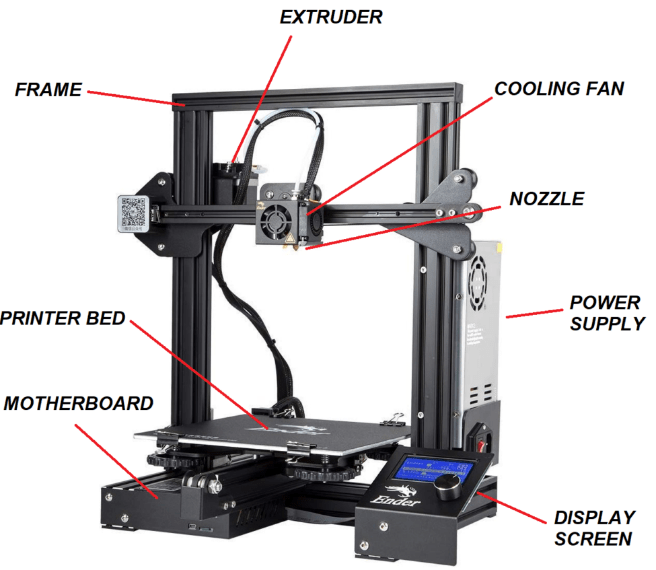
The Basics of an FDM 3D Printer
Frame
The frame is essentially the skeleton of your 3D printer. It provides the necessary support and rigidity to ensure accurate printing. Frames are often made from metal, acrylic, or wood. A sturdy frame minimizes vibrations and contributes to the overall print quality.
Extruder
The extruder is responsible for feeding the filament into the hot end, where it gets melted and deposited layer by layer. There are direct drive and Bowden extruders. In a direct drive extruder, the filament is pushed directly into the nozzle, while in a Bowden extruder, the filament travels through a tube before reaching the hot end.
Hot End
The hot end is where the magic happens. It heats the filament to a high temperature, melting it so it can be extruded through the nozzle. The hot end typically comprises a heating element, a temperature sensor, and a nozzle. Different materials require different temperatures, so having a good hot end is crucial.
Nozzle
Attached to the hot end, the nozzle is a small, typically interchangeable, component that determines the thickness of the extruded filament. They’re generally made of brass, but other materials like hardened steel or ruby-tipped nozzles are available for more abrasive filaments.
Build Plate
The build plate is where the printed object forms. It moves along the Z-axis in some printer designs and must be made of a material that allows the print to stick during printing but can be easily removed afterward. Build plates may be heated or non-heated, depending on the requirements of the filament being used.
Motors
Motors move the various parts of the printer. Stepper motors, in particular, are essential because they allow for precise control over movement. You’ll find motors controlling the X, Y, and Z axes as well as the filament extruder.
Belts and Screws
Belts and screws translate the rotational movement from motors into linear movement, allowing for the accurate positioning of the print head and build plate. It’s important to ensure these are well-maintained and free from wear.
Control Board
The control board is the brain of the 3D printer. It communicates with all other components, sending instructions to move the motors, heat the extruder, and manage the print process. Many control boards can be customized with firmware to enhance functionality.
Power Supply
Without power, nothing works! The power supply unit (PSU) provides the necessary electricity to different components. It’s essential to have a reliable PSU to prevent any disruptions during printing.
Features and Options in 3D Printers
Heated Bed
What It Is Used For
A heated bed helps in reducing warping by keeping the print adherence as the material shrinks upon cooling. This is particularly important when printing with materials like ABS, which are prone to warping.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Reduces warping and improves first-layer adhesion.
- Allows printing with a wider range of materials.
Cons:
- Increases the power consumption.
- Can take additional time to heat up, delaying the start of the print.
Automatic Bed Leveling
What It Is Used For
Automatic bed leveling makes sure that the build plate is perfectly level before starting the print. This is crucial for achieving a consistently good first layer, which can significantly impact the overall print quality.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Saves time and reduces the hassle of manual leveling.
- Improves first-layer adhesion and overall print quality.
Cons:
- Adds to the cost of the printer.
- May involve a learning curve or initial setup challenges.
Dual Extruders
What It Is Used For
Dual extruders allow you to print with two different filaments simultaneously. This can be used for multi-material prints, such as combining rigid and flexible materials, or printing with two different colors.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Enables complex, multi-material, or multi-color prints.
- Can improve print quality by using a different support material.
Cons:
- More mechanical complexity and higher cost.
- Increased chances of extruder maintenance issues.
Enclosed Build Chamber
What It Is Used For
An enclosed build chamber helps to maintain a stable temperature around the print, which is beneficial for reducing warping and improving overall print quality.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Provides a stable printing environment.
- Reduces exposure to potentially harmful fumes.
Cons:
- Can limit the size of objects you can print.
- The enclosed space can make it harder to monitor the print.
Touchscreen Interface
What It Is Used For
A touchscreen interface provides a more user-friendly and intuitive way to control the printer’s functions. This can make setup and adjustments simpler, particularly for beginners.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Easier and more intuitive to use.
- Often provides more functionalities and feedback.
Cons:
- Can make the printer more expensive.
- Touchscreens can be less durable than physical buttons in harsh environments.
Filament Sensor
What It Is Used For
A filament sensor detects if the filament runs out during a print. When this happens, it pauses the print so you can reload, helping to avoid failed prints.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Reduces the risk of failed prints due to running out of filament.
- Can save time and material by preventing wasted prints.
Cons:
- Adds to the cost of the printer.
- A malfunctioning sensor could cause false positives.
Wi-Fi Connectivity
What It Is Used For
Wi-Fi connectivity allows you to control and monitor your 3D printer remotely via an app or a web interface. This adds a layer of convenience and flexibility to your printing process.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Enables remote monitoring and control.
- Can provide automatic updates and software improvements.
Cons:
- Adds to the complexity and potential points of failure.
- Requires a stable internet connection for reliable performance.

Conclusion
Understanding the key parts of a hobby 3D printer can make your 3D printing experience smoother and more enjoyable. Each component, from the frame to optional features like Wi-Fi connectivity and dual extruders, plays a vital role in the performance and versatility of the machine. Knowing the pros and cons of each optional feature can help you make informed decisions when selecting or upgrading your 3D printer, ensuring it fits your specific needs and preferences. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to enhance your current setup, a well-informed choice can significantly impact your printing success.